- Other methods
- Other Properties
- Materials Science
[Analysis Example] Calculation of pressure and porosity in the forming process (calendaring) of battery electrodes
Compression and elongation simulation of solid (powder) layer by particle method (DEM)
Objectives and Methods
In the manufacturing process of battery electrodes, there is a process called calendering, in which electrode materials are compressed and formed by rollers. This process improves battery performance by forming the material into a uniform thin film and increasing the contact area between materials. Porosity and pressure are used as indicators of this process. In this case study, we present a simulation of solid particles (powders) forming assuming the calendering process.
VSOP-PS, one of the engines of J-OCTA, uses the Discrete Element Method (DEM=Discrete Element Method) to calculate pressure and porosity during thin film formation considering the contact between solid particles. For the material model, 6 types of active materials and 1 type of binder are used as particles with different diameters, based on the previous study. Compression calculations are performed by filling the closed region with particles and then lowering the upper wall. The porosity is obtained by subtracting the volume of the particles from the volume of the calculation area. As in the previous study, the relation between pressure and porosity is obtained by compressing to the maximum pressure and then elongating the upper wall upward.
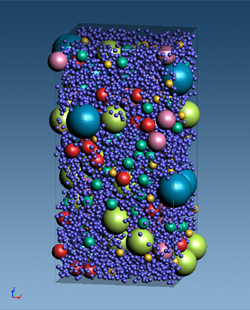 Figure1. Initial particle structure calculated with J-OCTA's RVE modeler
Figure1. Initial particle structure calculated with J-OCTA's RVE modeler
Results
Figure 2 plots the relation between the pressure applied to the upper wall and porosity during the elongation process. The results of VSOP-PS(blue circles) are close to the experimental and calculated results of the previous study.
Please contact us if you are interested in contact (friction) calculations using the discrete element method for solid and powder materials with VSOP-PS.
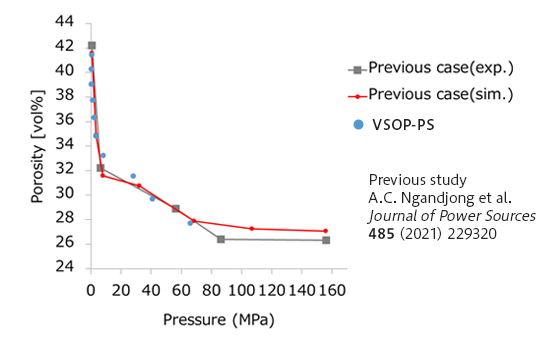 Figure2. Relation between pressure and porosity on the upper wall during the elongation process
Figure2. Relation between pressure and porosity on the upper wall during the elongation process
- Related Functions
- VSOP-PS (Particle Simulation)


