- Full Atomistic MD
- Small molecule penetration / diffusion / adsorption
- Materials Science
![]() User Only
User Only
Gas Diffusion Analysis
The permeability of small (gas) molecules in a polymer matrix is extremely important in the manufacturing of products such as film or contact lenses. The simulation of the small molecule's permeability for these types of polymers has recently drawn a significant amount of attention.
Using COGNAC, a MD simulator, it is possible to evaluate the diffusion properties of a small molecule in an amorphous polymer (diffusion coefficient).
Evaluation of Diffusion Coefficient of Oxygen in Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) (Reference [3])
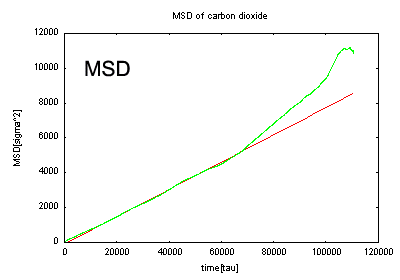 MSD of carbon dioxide
MSD of carbon dioxide
| Diffused Molecule | Calculation Result [cm^2/s] (300 [K]) |
Experimental Data [cm^2/s] [2] (308 [K]) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon dioxide | 2.65E-05 | 2.63E-05 |
| Oxygen | 5.61E-05 | 3.96E-05 |
The diffusion coefficient was calculated for oxygen molecules in the PDMS used as material for contact lenses and other similar items. For comparison, the diffusion coefficient of carbon dioxide has also been calculated.
In this simulation, we have succeeded in obtaining calculated values close to the experimental values. These MD diffusion coefficient estimations are used more as a tool to postulate changes in diffusion behavior after making changes to the diffusion molecules or polymer matrices; the quantitative values of the result are not of so much importance. In this case, the diffusion coefficient of oxygen is higher than that of carbon dioxide, which matches the experimental data. Thus, the MD calculations are qualitatively coincident with the experimental data.
Evaluation of Diffusion Coefficients for Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen Molecules in Cis-1,4-Polyisoprene
| Diffused Molecule | Calculation Result [cm^2/s](300[K]) |
Experimental Data [cm^2/s] [2] (298 [K] - 323 [K]) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon dioxide | 1.27E-06 | 1.05E-6 ~ 3.2E-6 |
| Oxygen | 7.55E-06 | 1.75E-6 ~ 4.9E-6 |
The diffusion coefficient was calculated for carbon dioxide and oxygen molecules in cis-1,4-polyisoprene, which is often used in rubber material. The results from the carbon dioxide are nearly coincident with the experimental data. The oxygen results are slightly high, but the overall relationship between the diffusion coefficients of carbon dioxide and oxygen are coincident with experimental data.
Evaluation of Diffusion Coefficients of Methane in Polyisoprolene
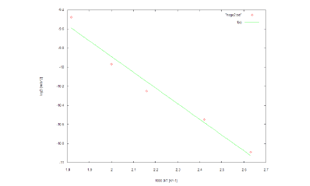
Here, we evaluate the temperature dependency of the diffusion coefficients. The X- axis is 1000/T (where T is temperature), and the Y-axis is the log of the diffusion coefficient (log D). The results indicate a linear relationship. This calculation result is a near-perfect reproduction of the results found in Reference [1].
- Reference
- [1] Jie Han and Richard H. Boyd, Polymer, vol. 37, 10, pp. 1797, 1996
- [2] Polyinfo Database Extracts
- [3] Y. Tamai, H. Tanaka and K. Nakanishi, Macromolecules, vol. 27, pp. 4498, 1994


