- Full Atomistic MD
- Interface / Phase Separation / Particle Dispersion
- Materials Science
- Life Science
![]() User Only
User Only
Evaluation of Interfacial Tension Using MD
The interface tension of water/octane has been evaluated by performing MD calculations using the full atomistic model. Water calculations were made using the SPC-FW model. Octane was calculated using J-OCTA modeling (GAFF was used for the force-field values, and MO calculations were used for the charge values). The MD calculations were made using our solver VSOP. As Figure 1 shows, after performing relaxation calculations using an NPT ensemble for both water and octane, a system with an interface was created by merging the water and octane systems together.
After the interface was created, calculations were performed using an NVT ensemble. The post-relaxation stress values were used in the following formula to evaluate the interface tension. Figure 2 shows the changes in interface over time in a relaxed state. Although the interface tension results have large fluctuations, when time-averaged values are taken, the evaluated results were 53.3 [dyn/cm]. This compares well to the experimental data values of 51.7 [dyn/cm] [1].

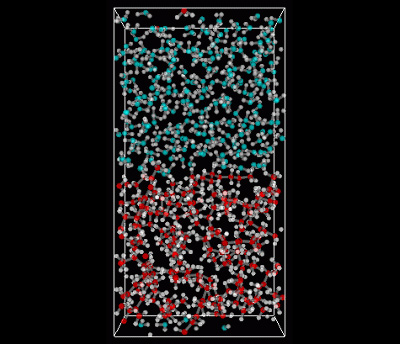 Figure 1. Interface Model (Upper area: water, lower area: octane)
Figure 1. Interface Model (Upper area: water, lower area: octane)
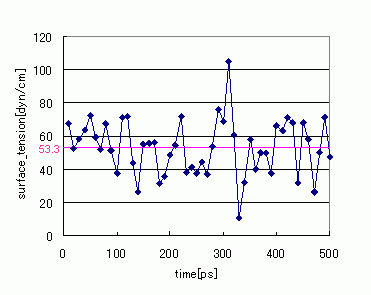 Figure 2. Changes in Interface Tension Over Time
Figure 2. Changes in Interface Tension Over Time
- Reference
- [1] A. Maiti and S. McGrother, J. Chem. Phys., 120, 3, 15 (2004)


