- DPD / Mean Field
- Interface / Phase Separation / Particle Dispersion
- Materials Science
Simulation of Solvent Evaporation Using DPD.
A simulation of polymer phase separation associated with solvent evaporation was conducted using COGNAC (DPD). Two polymer components, a solvent, and a gas phase were represented by DPD particles, and the evaporation phenomenon was represented by the solvent components moving into the gas phase region and changing into gas phase components.
For simplicity, Figure 1 shows only the two polymer components in yellow and red. The two components, which were mixed in the initial state due to the presence of the solvent, formed a phase-separated structure as the solvent evaporated. As a result, a phase-separated structure first formed parallel to the substrate, after which a phase-separated structure formed perpendicular to the substrate.
It is also possible to evaluate the change in the phase-separated structure for different conditions, such as interactions between components, the evaporation rate of solvent, and the wettability to the substrate. See Reference (1) for details on the calculation conditions.
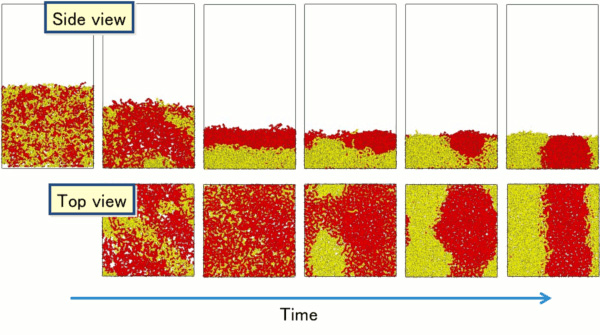 Fig. 1. Phase-separated structure of a polymer thin film caused by solvent evaporation.
Fig. 1. Phase-separated structure of a polymer thin film caused by solvent evaporation.
- Reference
- [1] Nihon Reoroji Gakkaishi, Vol.36, 93-98
- https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/rheology/36/2/36_2_93/_pdf