- DPD / Mean Field
- Continuum Model
- Multiscale Analysis
- Mechanical / Viscosity / Viscoelasticity
- Interface / Phase Separation / Particle Dispersion
- Materials Science
Dispersed Structure and Nonlinear Structural Analysis of Carbon Nanotubes
A simulation of the dispersed structure of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in the microphase separation of block copolymers is conducted. Calculations using the DPD included in COGNAC were conducted according to Reference (1).
The settings were such that CNTs are attracted to blue components and are repelled by light blue components, and the rigidity of CNTs was set by the angle potential.
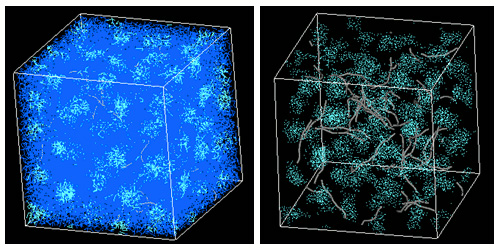 Fig.1 Polymer phase separation using DPD (left) and CNTs in the same system (right).
Fig.1 Polymer phase separation using DPD (left) and CNTs in the same system (right).
The DPD results (2D) were converted into mesh data (Fig. 2). Thin elements were placed at the interfaces between the CNTs and the polymer so that the interface parameters could be used in the Finite Element Analysis.
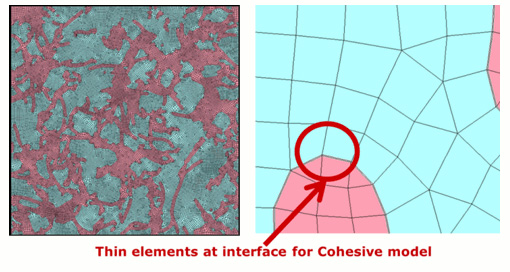 Fig. 2 2D mesh data created from DPD results. (Red region=CNTs, Blue region=polymer)
Fig. 2 2D mesh data created from DPD results. (Red region=CNTs, Blue region=polymer)
A nonlinear structural analysis with uniaxial elongation using LS-DYNA was conducted based on the created mesh (Fig. 3). The results indicate that, after separation occurs at the interfaces, the CNTs spread into the polymer regions and affect the stress-strain characteristics of the entire system.
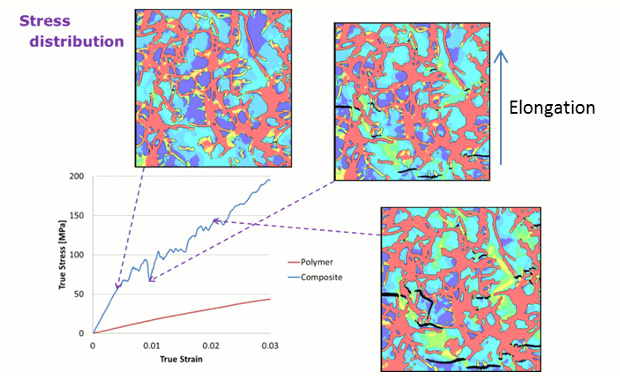 Fig.3 Stress distribution under elongation simulation with LS-DYNA.
Fig.3 Stress distribution under elongation simulation with LS-DYNA.
- Reference
- (1) Appl. Phys. Lett., 90, 033116, (2007)
- (2) T.Ozawa, The Japan Society for Computational Engineering and Science (JSCES) 17th Annual Conference, (2012)


