- Full Atomistic MD
- Thermal
- Materials Science
Simulation of Crosslinked Epoxy Resin.
Curing of an epoxy resin is simulated using the functions available in J-OCTA. Bisphenol A epoxy resin and ethylenediamine are the target molecules.
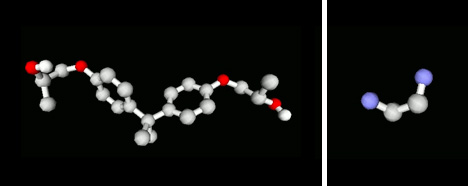 Fig. 1 Modeling of molecules using J-OCTA
Fig. 1 Modeling of molecules using J-OCTA
(left=EP, right=ethylenediamine)
 Fig. 2 Simulation of crosslinking reaction
Fig. 2 Simulation of crosslinking reaction
For the obtained cross-linked structure, the glass transition temperature (Tg) is evaluated using a function in the J-OCTA Case Studies Database. In this study, glass transition temperatures were calculated for the structures with cross-link densities of 29%, 50%, and 80%.
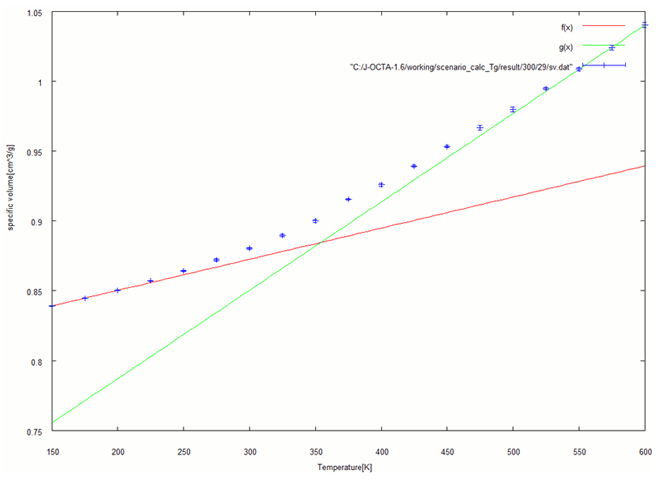 Fig. 3-a. Specific volume at each temperature (29%)
Fig. 3-a. Specific volume at each temperature (29%)
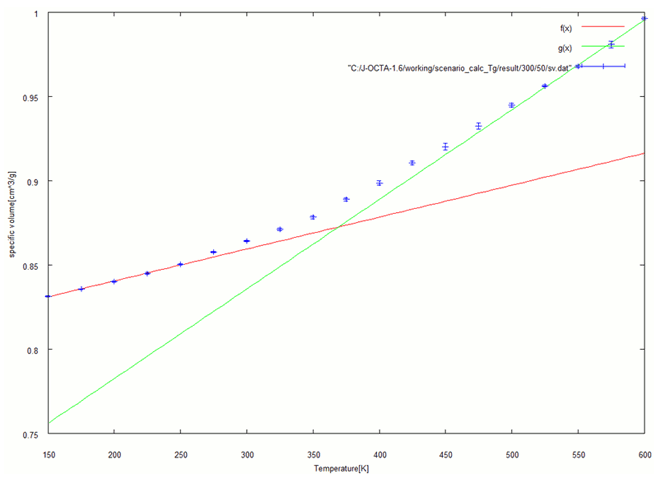 Fig. 3-a. Specific volume at each temperature (50%)
Fig. 3-a. Specific volume at each temperature (50%)
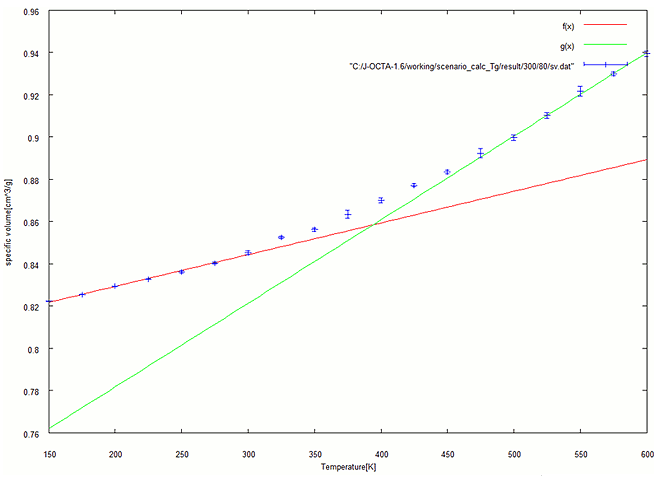 Fig. 3-b. Specific volume at each temperature (80%)
Fig. 3-b. Specific volume at each temperature (80%)
The specific volume was calculated at each temperature, and the relationship was linearly approximated for the low- and high-temperature sides. The glass transition temperature was determined to be the point of intersection between the two approximations. Fig. 3 shows the results in the range from 150 [K] to 600 [K].
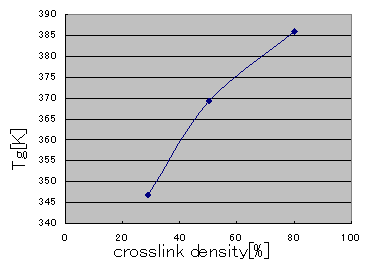 Fig. 4 Tg at each cross-link density
Fig. 4 Tg at each cross-link density
Only three cross-link densities were used in this study, but the results indicate that the glass transition temperature increases as the cross-link density increases.