- Full Atomistic MD
- Mechanical / Viscosity / Viscoelasticity
- Materials Science
Properties of Cross-Linked Phenolic Resins
courtesy of ![]()
Structure-property relationships of cross-linked phenolic resins have been studied using atomistic MD simulations. The cross-linked structures were prepared by crosslinking reactions of linear phenolic resin oligomers (9-mer). In this study, three cross-linked structures with degrees of crosslinking (D) of 70%, 82%, and 92% were investigatesd.
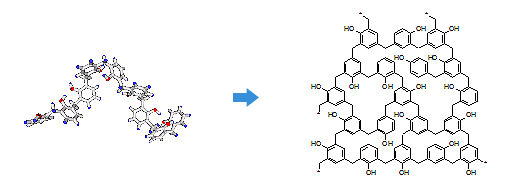 Fig.1 Crosslinking reaction model of phenolic resins.
Fig.1 Crosslinking reaction model of phenolic resins.
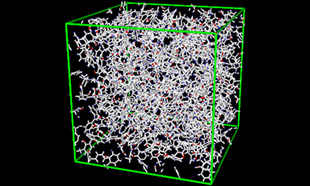 Fig.2 Structure of a cross-linked phenolic resin.
Fig.2 Structure of a cross-linked phenolic resin.
To evaluate the effect of D on the glass transition temperature (Tg), the specific volume was calculated as a function of temperature. As shown in Fig.3, an increase in D accompanies an increase in Tg. This indicates that segmental motions were suppressed by the cross-links.
In addition, to the estimate mechanical properties when the cross-linked structures are in a glassy state, uniaxial elongations were performed at 300 K. Fig.4 shows the calculated stress-strain curves, which indicate a clear dependence on D.
The details of this study are also described in ref.1.
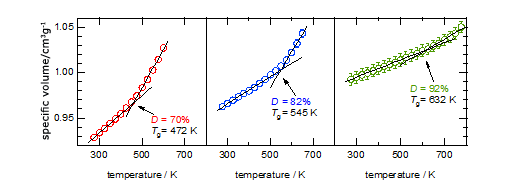 Fig.3 Change in specific volume: red, D = 70%; blue, D = 82%; green, D = 92%. The glass transition temperature of each structure was determined from the change in the slope.
Fig.3 Change in specific volume: red, D = 70%; blue, D = 82%; green, D = 92%. The glass transition temperature of each structure was determined from the change in the slope.
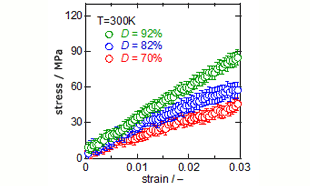 Fig.4 Stress-Strain Curves: red, D = 70%; blue, D = 82%; green, D = 92%.
Fig.4 Stress-Strain Curves: red, D = 70%; blue, D = 82%; green, D = 92%.
- Reference
- [1] A. Izumi, T. Nakao and M. Shibayama, Soft Matter, 2012, 8, 5283-5292.


