- Coarse Grained MD
- Continuum Model
- Multiscale Analysis
- Mechanical / Viscosity / Viscoelasticity
- Interface / Phase Separation / Particle Dispersion
- Materials Science
Fracture of CFRTP / Interface
Purpose and Method
We evaluated the effect of the interfacial property for different CFRTP fiber dispersion structures.
LS-DYNA was used for structural analysis. (Figure1)
To improve the strength of the interface between carbon fiber and resin, surface treatments of the carbon fiber are important. The interfacial property between fiber and resin were verified using Coarse Grained Molecular Dynamics. The trend of the interface strength with and without surface treatment was obtained. Young’s modulus and the yield stress were the same for both interfacial structures, but there was a difference in the behavior after yielding. (Figure2)
The results were considered in the FEM material (cohesive) model. The 2D fiber dispersion structures of UD material were created using Digimat. (Figure3)
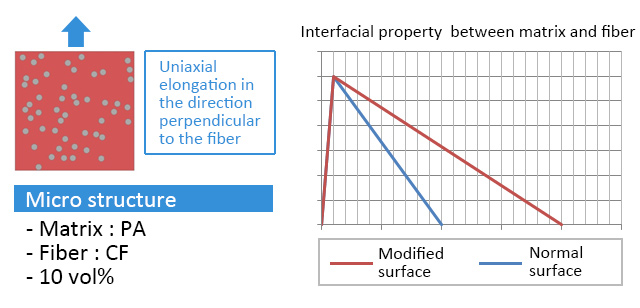 Figure 1. Simulation conditions for LS-DYNA
Figure 1. Simulation conditions for LS-DYNA
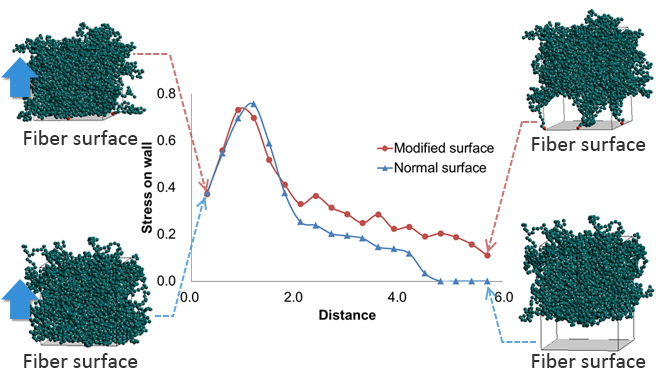 Figure 2. Evaluation of interfacial property by J-OCTA
Figure 2. Evaluation of interfacial property by J-OCTA
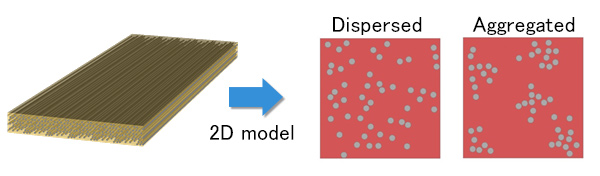 Figure 3. Dispersed and aggregated geometries were generated by Digimat-FE
Figure 3. Dispersed and aggregated geometries were generated by Digimat-FE
Simulation result
Microstructure affects the fracture behavior. The fracture behavior was different depending on the interfacial property and dispersion structure. In the case of “the normal surface and the aggregated structure”, the fracture progressed rapidly from de-bonded interfaces. On the other hand, the progress of fracture was most suppressed in “the modified surface and the dispersed structure”.
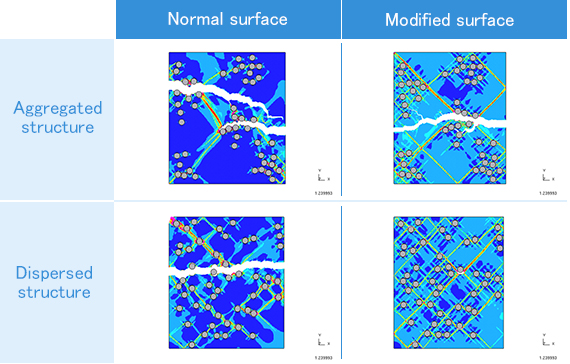 Figure 4. Calculation results of LS-DYNA
Figure 4. Calculation results of LS-DYNA


